Explore Quinoa: The “Golden” Grain
There is no doubt that breast milk provides your baby with the best nutritional start to life. Read the article to know more.
There is no doubt that breast milk provides your baby with the best nutritional start to life.1 However, once your baby reaches six months of age, his or her nutritional needs start to exceed what can be provided by breast milk.2 In many countries around the world, infant cereals are the first ‘solid’ food to be introduced to a baby’s diet.3 Cereals are an excellent source of energy, providing many of the additional nutrients your growing baby needs.4
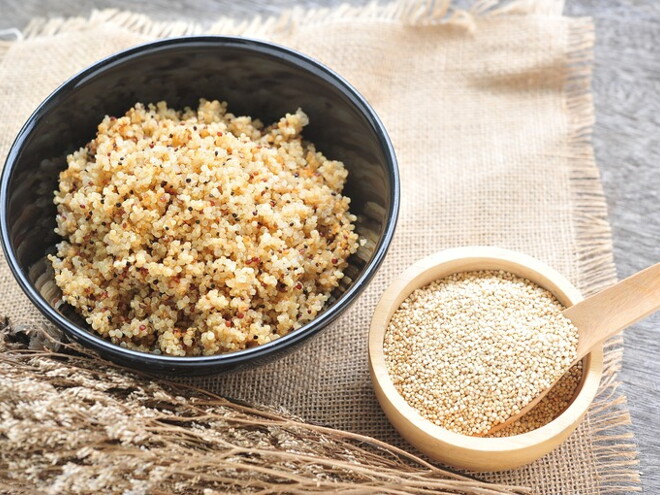
QUINOA: THE SUPERGRAIN OF THE FUTURE
It has taken the world a long time to fully understand and appreciate the significant health benefits of Quinoa. It is a valuable addition to any fortified infant cereal. Regarded as a superfood5,6 quinoa is a starchy seed that resembles other cereal grains, but has superior nutritional qualities and health benefits.5,7 In fact, the nutritional benefits of quinoa have even been recognised by NASA, who include it as part of the standard diet of their astronauts.8
SALIENT FEATURES OF QUINOA
Nutrient-Rich:
Quinoa contains a complex mix of macronutrients (carbohydrates, fats and proteins) and micronutrients (minerals and vitamins).8
Balanced Composition:
Different food types contain different proportions of nutrients; but quinoa is considered unique because it has an optimal balance of nutrients and essential amino acids (those that our body cannot produce). There are nine essential amino acids and quinoa contains all of them.5,9
Immune Boost:
Quinoa also has immune-supporting properties due to the exceptionally high levels of amino acids (protein building blocks) and being naturally high in Iron.5,10
Antioxidant:
Quinoa contains antioxidants, called flavonoids.7 An antioxidant prevents damage to healthy body cells, and a diet rich in antioxidants is considered to be healthy.11
Gluten-Free:
Quinoa is gluten-free.12 It is suitable for use by those who are sensitive to gluten, or have celiac disease and can significantly improve the nutritional content of a diet lacking gluten.13
Quinoa is the golden standard among grains. It makes absolute sense to include it as a dietary choice for your growing child.14
References:
1.Complementary feeding. WHO.
2.Fewtrell M, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017;64(1):119-132.
3.Freeman V, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000;31(SUPPL. 1):S76-85.
4.Klerks M, et al. Nutrients. 2019;11(2).
5.Angeli V, et al. Foods. 2020;9(2).
6.van den Driessche JJ, et al. Food Funct. 2018;9(4):1944-1966.
7.Abugoch James LE. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2009;58:1-31.
8.Rodríguez JP, et al. Front Genet. 2020;11.
9.What is Quinoa: Nutrional value. FAO.
10.Rao NK, et al. J Agric Environ Sci. 2012;12(10):1350-1355.
11.Antioxidants: In Depth. NIH: National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health.
12.Filho AMM, et al. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017;57(8):1618-1630.
13.Lee AR, et al. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2009;22(4):359-363.
14.Black RE, et al. Lancet. 2008;371(9608):243-260.